It’s a regrettable reality that there is never enough time to cover all the interesting scientific stories we come across each month. In the past, we’ve featured year-end roundups of cool science stories we (almost) missed. This year, we’ve experimented with a monthly collection. December’s list includes a fossilized bird that choked to death on rocks; a double-detonating "superkilonova"; recovering an ancient seafarer's fingerprint; the biomechanics of kangaroo movement; and cracking a dark matter puzzle that stumped fictional physicists on The Big Bang Theory, among other tantalizing tidbits
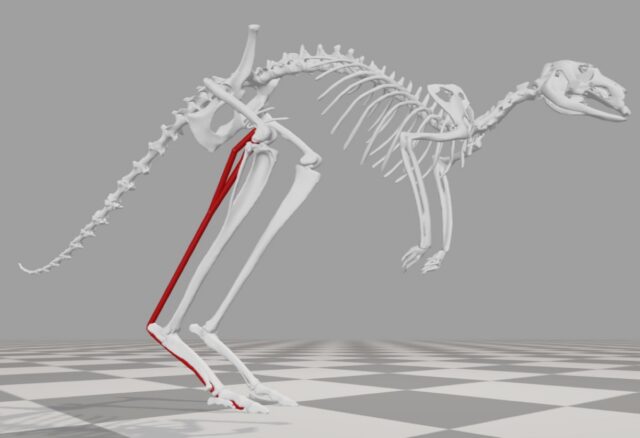
Secrets of kangaroo posture
 Credit:
Thornton et al., 2025/CC BY 4.0
Credit:
Thornton et al., 2025/CC BY 4.0
Kangaroos and wallabies belong to a class of animals called macropods, with unique form and style of movement. Their four limbs and tail all contact the ground at slow speeds, while they use a hopping gait at higher speeds. Typically, high-speed movements are more energy-intensive than slow-speed motion, but the opposite is true for macropods like kangaroos; somehow the hopping speed and energy cost become uncoupled. According to a paper published in the journal eLife, this may be due to changes in a kangaroo's posture at higher hopping speeds.
